
In the mining and aggregate industry, equipment selection is the most critical factor determining your project's profitability. A well-configured crushing line runs smoothly with minimal downtime and low wear costs. A poorly configured one becomes a money pit—plagued by bottlenecks, frequent breakdowns, and poor product quality.
Many operators ask: "Which crusher is the best?"
The honest engineering answer is: "It depends on your rock."
Whether you are crushing granite for highway asphalt, processing wet coal for power plants, or making manufactured sand, the equipment must match the material. This guide breaks down the four main stages of crushing and helps you navigate the choices between Jaw, Cone, Sizer, and VSI crushers to build a high-ROI production line where consistent performance depends on durable stone crusher machine spare parts.
Before looking at any machine catalog, you must understand the physical properties of your raw material. Three key factors dictate your equipment choice:
1.Mohs Hardness & Abrasiveness:
Hard/Abrasive (Granite, Basalt, River Pebble): Requires compression crushers (Jaw, Cone) that use high-manganese steel parts.
Soft/Brittle (Limestone, Coal): Can be handled by shear or impact forces (Sizer, Impact Crusher).
2.Moisture Content:
Dry rock is easy. But if your material contains clay or moisture (>10%), standard compression crushers will clog, halting production.
3.Feed Size vs. Output Size:
The "Reduction Ratio" determines if you need a two-stage or three-stage plant.
The primary crusher is the "gatekeeper." Its job is simple but brutal: take large, irregular Run-of-Mine (ROM) stones and reduce them to a manageable size (usually <150mm) for the conveyor belts.
The Industry Standard: Jaw Crusher
For almost all hard rock and quarry applications, the Jaw Crusher is the undisputed king of primary crushing.
Why choose it: It relies on simple compressive force. The deep crushing cavity allows for a massive feed size and high capacity.
Key Feature: Our Jaw Crushers feature a deep cavity design that improves feeding efficiency and creates a higher crushing ratio, reducing the load on the next stage.
This is where many plant designs go wrong. The choice of secondary crusher depends entirely on your material's hardness and stickiness.
Scenario A: Hard & Abrasive Rock (Granite, Basalt)
The Solution: Hydraulic Cone Crusher ,If you are processing hard rock, Impact Crushers will suffer from rapid blow bar wear, destroying your profit margins.
The Advantage: The Cone Crusher uses "lamination crushing" (rock-on-rock) principles. This not only handles high hardness with lower wear costs but also produces a better grain shape for concrete aggregates.
Technology: Modern hydraulic systems allow for automatic tramp iron release, preventing damage from non-crushable materials.
Scenario B: Wet, Sticky, or Soft Material (Coal, Clay)

The Solution: Sizer Crusher (Twin-Tooth Roll) ,Using a Cone Crusher for wet coal or sticky clay is a recipe for disaster—it will block instantly.
The Advantage: The Sizer Crusher uses high-torque, low-speed shearing force. Its intermeshing teeth actively clear the material, making it immune to clogging. It is the gold standard for coal mines and power plants.
If your goal is to produce Manufactured Sand (M-Sand) or high-grade aggregates for infrastructure, you need a third stage.
The Shaper: VSI Crusher (Vertical Shaft Impact)
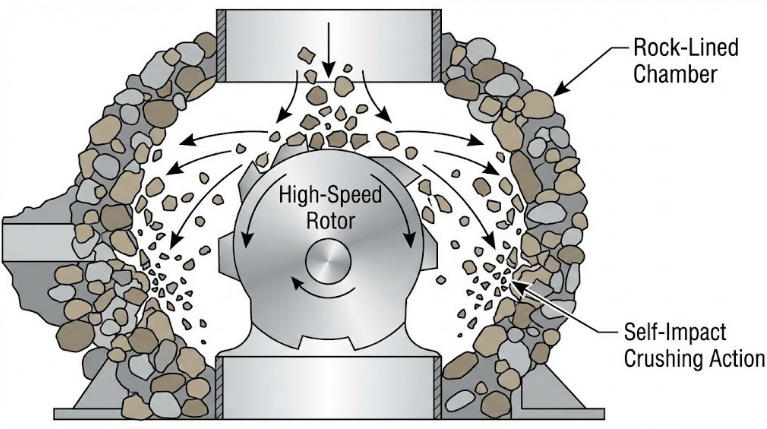
Secondary crushers can leave micro-cracks in the stone or produce flaky particles. The VSI Crusher corrects this.
How it works:It accelerates stone to high velocities and smashes it against a rock lining ("Rock-on-Rock").
The Result: This action rounds off sharp edges, creating perfectly cubical sand and gravel that meets the strictest standards for high-strength concrete.
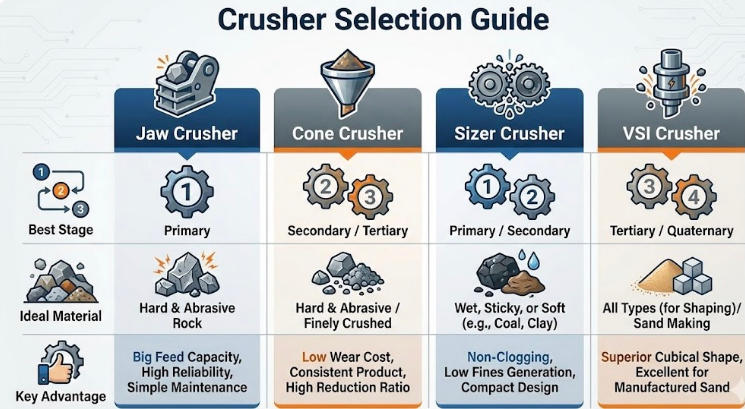
To simplify your decision, refer to this quick comparison guide:
Crusher Type | Best Stage | Ideal Material | Key Advantage |
Jaw Crusher | Primary | All Rock Types | Handles large feed size; High reliability. |
Cone Crusher | Secondary | Hard / Abrasive | Low wear cost; Excellent reliability. |
Sizer Crusher | Primary/ Secondary | Coal / Wet / Sticky | Non-clogging; Low fines generation. |
VSI Crusher | Tertiary | All (for Shaping) | Produces Cubical M-Sand; Superior shape. |
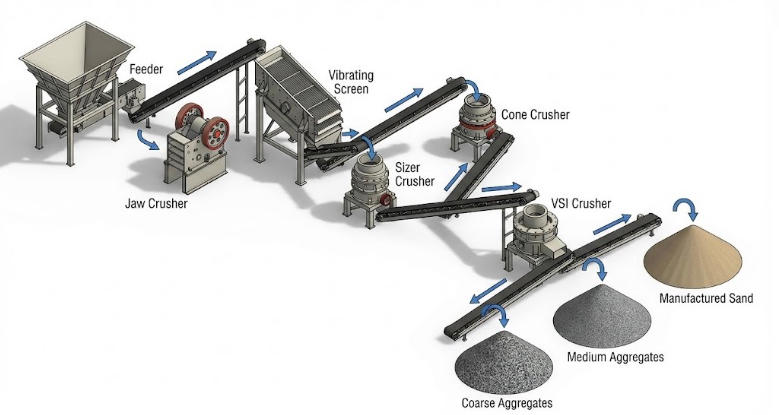
Selecting a crusher is not just about buying a machine; it is about designing a process flow. A Jaw Crusher paired with the wrong secondary unit can bottleneck your entire operation.
At Sichuan BENO Energy Conservation and Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. , we don't just sell equipment; we engineer solutions. Whether you need a standalone Sizer for a coal project or a complete Jaw-Cone-VSI circuit for a granite quarry, our team ensures the configuration matches your specific mineralogy and budget.
Stop guessing. Send us your raw material details and capacity requirements. Our engineers will provide a Free 3D Flow Chart Design and a detailed ROI analysis for your project.